For more information on interval funds, check out our affiliate site: Interval Fund Tracker
The defining features of an interval fund are as follows
- A continuously offered closed end fund.
- Required to repurchase between 5% and 25% of shares at NAV at predetermined intervals(usually quarterly).
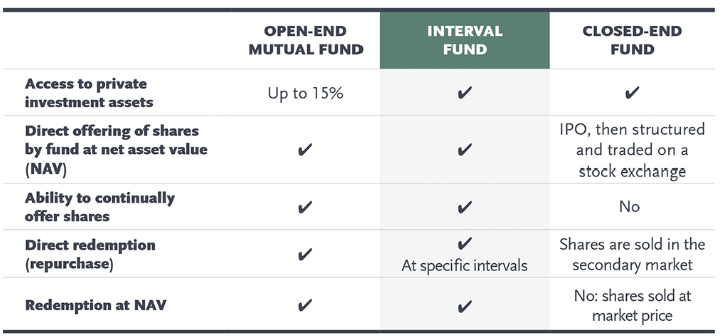
An interval fund is a professionally managed, pooled investment vehicle that combines attractive features of both closed-end funds and traditional open-end funds. Interval funds offer their shares on a continuous basis, rather than in a one time IPO. The following table summarizes how interval funds compare to other common types of investments:
Interval Fund History
Interval funds may seem like a new concept, but they originally came into existence as a result of a SEC recommendation in its landmark 1992 study : “Protecting Investors: A Half Century of Investment Company Regulation.” This study concluded that the rigid delineation between “open end” funds, providing daily liquidity, and “closed end funds” , which do not offer daily liquidity, limited the ability of sponsors to offer innovative investment products to investors:
The Division has concluded it would be appropriate to provide the opportunity for investment companies to chart new territory between the two extremes of the open-end and closed-end forms, consistent with investor protection.
Liquidity
Interval funds generally don’t list their shares on any exchange(with a few exceptions). Other closed end funds may have repurchases programs adopted in the board’s discretion. However, interval funds can only eliminate their repurchase plans with shareholder approval.
Rule 23c-3 under the 1940 Act, known as interval fund rule was adopted in 1993. The interval fund rule requires that interval funds offer to repurchase between 5% and 25% of shares at NAV at predetermined intervals(quarterly, semi-annually, or annually). The rule also requires that interval funds provide advanced notice to shareholders between 21 and 42 days in advance of repurchase offer . Interval Funds also file N-23c-3 with the SEC within 3 days of sending shareholder notification of a tender offer.
Interval Fund Strategies
A wide variety of investment strategies can work in an interval fund structure.
The most popular include:
Many major alternative investment managers, REIT and BDC sponsors have registered interval funds in recent years For info, see our database of new fund launches.
Transparency
All unlisted closed end funds are registered under the 1940 act, and therefore must provide regular updates in SEC filings. On a semi annual basis, unlisted closed end funds file detailed financial statements on form N-CSR. These semi annual reports must be accompanied by certification by key executives. In their first and third fiscal quarters, both interval and tender offer funds must file form N-Port, which contains monthly portfolio holdings. As a result, investors have a transparent view of how the fund manager is implementing their strategy.
An asset manager launching an interval or tender offer fund must be prepared to keep up with ongoing reporting requirements.
Factors Driving the Growth of Interval Funds
A variety of regulatory and market pressures are driving the growth of interval funds. However, lack of data makes it difficult for investors to evaluate choices. Therefore, the purpose of Interval Fund Tracker is to increase transparency by providing comprehensive information to market participants. Furthermore, this site provides competitive intelligence and research services to asset managers.
Other Resources
Interval Fund Tracker is our affiliate site dedicated to the interval fund sector.